Introduction to Ceramic Foam
Ceramic foam is a lightweight, porous material with a three-dimensional network structure. It combines the inherent properties of ceramics, such as high temperature resistance and chemical stability, with the unique advantages of foam materials, like low density and high porosity. The material is widely used in filtration, insulation, and catalyst support due to its excellent thermal and mechanical properties

Key Characteristics of Ceramic Foam
The defining feature of ceramic foam is its high porosity, which can range from moderate to extremely open structures. This porosity allows for fluid permeability and thermal insulation while maintaining structural integrity. The material can be made from various ceramic compositions, including alumina, zirconia, and silicon carbide, depending on the intended application. Its cellular structure provides a large surface area, making it useful in processes requiring efficient mass transfer.
General Manufacturing Process of Ceramic Foam
The production of ceramic foam involves several key steps, starting with the preparation of a ceramic slurry or precursor. The slurry is then foamed using physical or chemical methods to create a porous structure. After shaping, the green body undergoes drying and sintering to achieve the final ceramic foam. The choice of raw materials and foaming techniques significantly influences the properties of the end product.
Slurry Preparation
The first step in making ceramic foam is preparing a homogeneous slurry. This typically involves mixing ceramic powders with water or organic solvents, along with binders and additives to improve rheology. The slurry must have suitable viscosity to ensure proper foaming and shaping. Careful control of particle size distribution and solid loading is essential to achieve a stable and uniform mixture.

Foaming Techniques
Several foaming methods can be employed to create the porous structure in ceramic foam. Physical foaming involves introducing gases mechanically or through pressure release, while chemical foaming relies on gas-generating reactions. Another approach uses sacrificial templates, where a fugitive material burns out during sintering, leaving behind pores. Each technique offers distinct advantages in terms of pore size distribution and structural control.
Shaping and Forming
After foaming, the material must be shaped into the desired form before solidification. This can be done through casting, extrusion, or molding, depending on the application requirements. The green body must maintain its structural integrity during this stage to prevent collapse of the foam network. Proper shaping ensures uniformity and minimizes defects in the final product.
Drying Process
Drying is a critical step to remove moisture or solvents from the green body without causing cracks or distortions. Controlled drying conditions, such as temperature and humidity, are necessary to prevent rapid shrinkage or uneven stress distribution. Slow and uniform drying helps preserve the porous structure and prepares the material for sintering.
Sintering and Final Processing
Sintering involves heating the dried foam at high temperatures to densify the ceramic struts and enhance mechanical strength. The temperature profile must be carefully optimized to avoid excessive shrinkage or pore collapse. After sintering, additional treatments like coating or surface modification may be applied to tailor the foam for specific applications.
Applications of Ceramic Foam
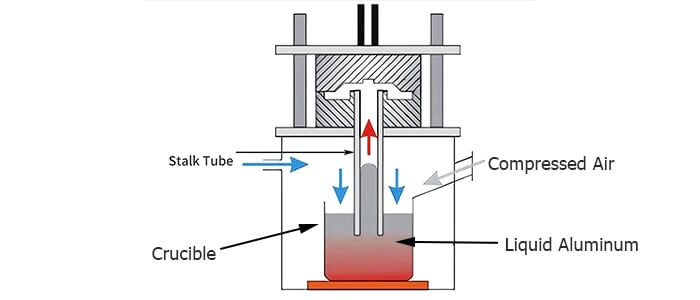
Ceramic foam finds use in diverse industries due to its unique properties. It serves as filters for molten metals, supports for catalytic reactions, and insulating materials in high-temperature environments. The material’s versatility continues to drive research into new formulations and manufacturing techniques for enhanced performance.SEFU has been committed to producing high-quality foam ceramics to provide users with the best use experience.
Conclusion
The production of ceramic foam involves a series of carefully controlled steps to achieve the desired porous structure and properties. With its wide range of applications and ongoing technological advancements, ceramic foam remains an important material in both traditional and emerging industries. Understanding the manufacturing process is key to optimizing performance for specific needs.