In the casting production process, the alumina ceramic filter is often the least valued but most important link. This seemingly simple ceramic component actually directly affects the internal quality and surface finish of the casting. When many foundries encounter quality problems, they often give priority to adjusting the smelting process or modifying the mold design, but ignore the key role of the filter.

Basic principles of filter selection
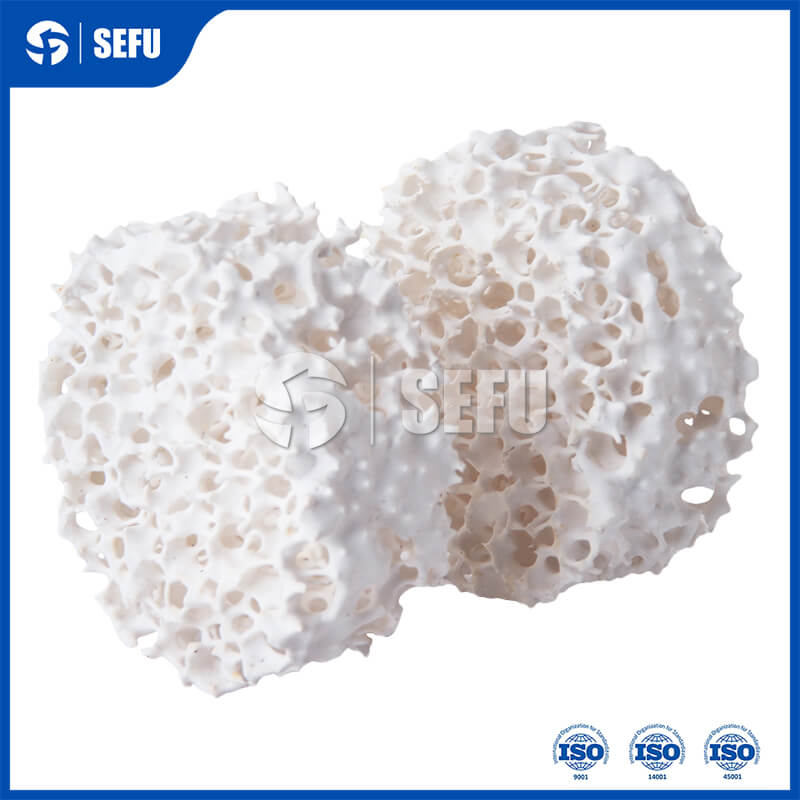
The working principle of alumina ceramic material filters is far more than simple physical interception. When the metal melt flows through the three-dimensional mesh structure, complex physical and chemical reactions occur at the same time. High-quality filters can capture micron-sized inclusions through surface adsorption, which is impossible for ordinary screen filters. The filtering effect depends not only on the nominal accuracy, but also on the uniformity of the pore structure.
Analysis of common selection misunderstandings
Many foundries are prone to several typical misunderstandings when selecting filters.
- Excessive pursuit of high precision and neglect of fluidity often leads to insufficient pouring. Excessive filtration accuracy will significantly increase the flow resistance of the molten metal and produce an unfavorable pressure drop in the pouring system.
- Only focusing on the initial cost and ignoring the service life, low-priced products may cut corners in key links such as raw material purity and sintering process, and their pore uniformity and high-temperature strength are difficult to guarantee, which will eventually increase the overall cost.
- Neglecting preheating procedures causes alumina ceramic material to develop thermal shock cracks, which will seriously affect the final filtration effect. What’s worse, this damage has a cumulative effect. As the number of uses increases, the performance of the filter will decay faster and faster.

- Random selection of filter size. Too small a filtration area will increase the local flow rate, aggravate the erosion of the filter structure, and shorten its service life.
- Ignoring the sealing of the filter installation. Even if a high-quality filter is selected, if there are gaps or poor sealing during installation, the metal liquid will pass through the bypass, making the filtration process meaningless.
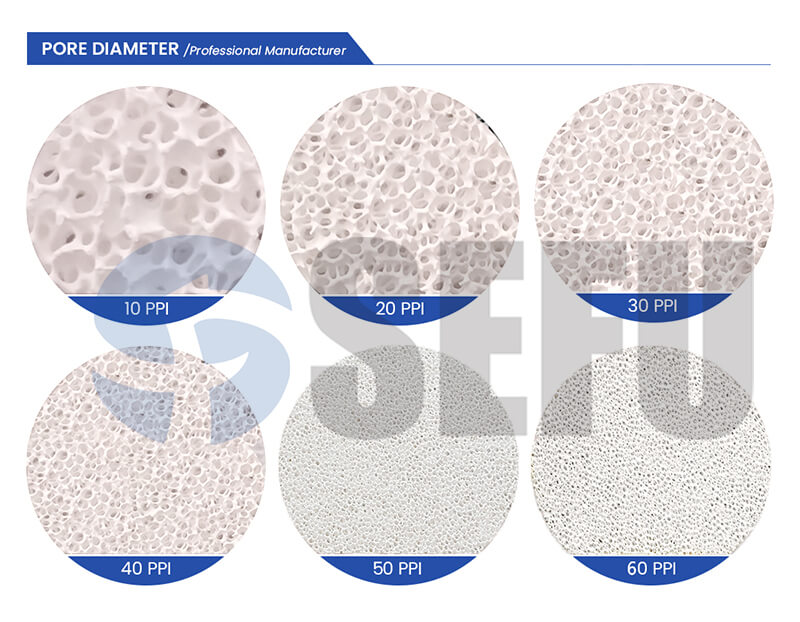
The practical significance of key parameters
As an important parameter of the filter, the PPI value needs to be reasonably selected according to the specific application scenario. Filters with different PPI values have significant differences in flow capacity and filtration accuracy. The more advanced gradient pore design can take into account both flow and filtration effect, and achieve optimal performance through graded filtration. At the same time, alumina ceramic purity and thermal shock resistance also need to match the production process.
Precautions during use
The performance of alumina ceramic material filters depends largely.on the control of operational details. Negligence in any link may lead to failure.
- The preheating link needs special attention. It is necessary to use a gradual heating method to allow the filter to slowly transition from room temperature to a temperature close to the molten metal. Avoid rapid heating to catch up with the progress, which is very likely to cause thermal stress cracks.
- The installation process must also be careful. The sealing performance of the filter directly affects the filtering effect, and suitable sealing materials must be selected. During installation, ensure that the force is evenly distributed around. Any eccentric load may cause the filter to break.
- The flow rate of the molten metal needs to be strictly controlled during use. The flow rate beyond the design range will significantly reduce the filtration efficiency. In actual operation, if the molten metal passing time is significantly extended or the casting quality fluctuates, the filter status should be checked immediately.
- The professional quality of the operator is also critical. Systematic training is required before taking up the job. The training content should not only include standard procedures, but also emphasize the identification and handling of abnormal situations. Regularly organizing practical assessments can ensure that the operating specifications are implemented.
In the pursuit of high-quality castings, every detail cannot be ignored. Alumina filters are the last line of defense for molten metal and are a very important link. The correct selection and use of filters can often achieve significant quality improvements with minimal investment, which is the most economical quality solution.