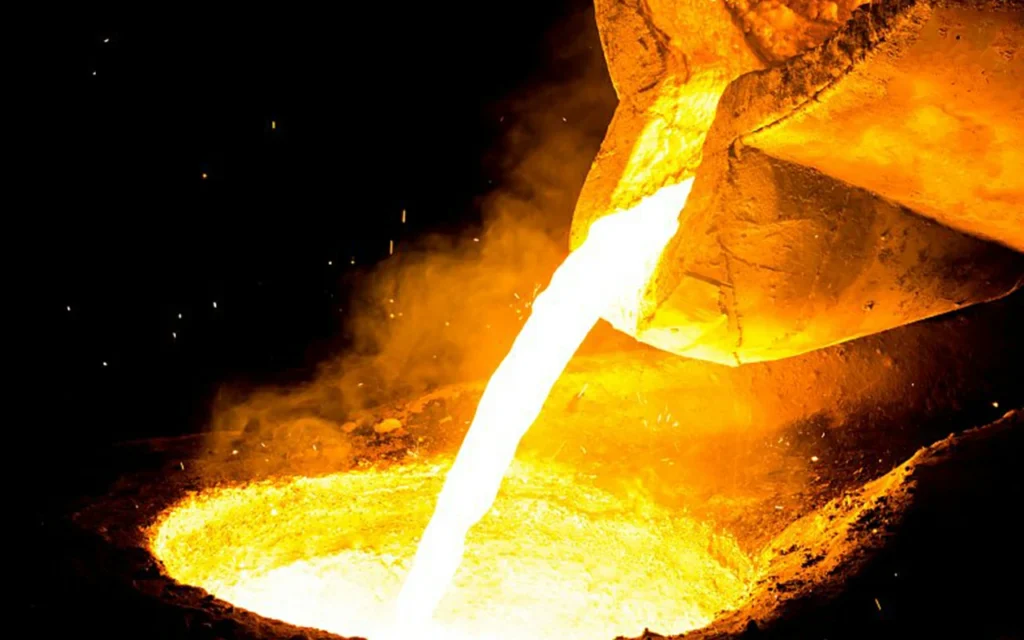
Among all components of a casting system, the runner holds a particularly important position. The runner serves as a critical bridge between the sprue and mold cavity, directly impacting casting quality. Understanding the function and design principles of runners is fundamental to mastering casting technology.

Definition and Basic Concept
In casting terminology, a runner refers to the passage that guides molten metal flow. It is typically positioned after the sprue and before the gates. Its primary task is to deliver molten metal smoothly into the mold cavity. A well-designed runner can prevent various flow-related issues during casting.
Historical Development
The evolution of runner technology is closely tied to the development of casting processes. From ancient simple trench runners to modern complex systems, runner technology has continuously advanced. After the Industrial Revolution, runner design became more scientific with increasing demands on casting quality. Recently, computer simulation technology has elevated runner design to new levels.
Primary Functions
The runner performs multiple critical functions in the casting process. Firstly, it controls the flow speed and direction of molten metal. Secondly, the runner helps reduce turbulence during metal flow. Moreover, proper runner design effectively prevents gas entrapment and oxidation. Finally, the runner also affects the solidification process and feeding efficiency of castings.
Material Selection
The choice of runner material depends on the specific casting process. Traditional sand casting typically uses molding sand for runners. Permanent mold casting may use cast iron or steel runners. Modern innovative materials like ceramic and paper runners are gaining wider applications. Different materials have their own advantages and disadvantages, requiring careful selection.SEFU company produces products such as paper runners
Technological Innovations
Modern runner technology is undergoing significant transformations. Computer-aided design enables more precise runner optimization. 3D printing offers new possibilities for complex runner manufacturing. Smart monitoring systems can track molten metal flow in real time. These innovations are driving casting processes toward greater efficiency and precision.
Environmental Considerations
With growing environmental awareness, sustainability has become a consideration in runner design. The use of recyclable materials reduces waste in casting processes. Optimized designs can reduce energy consumption and emissions. Green casting concepts are influencing the direction of runner technology development.
Conclusion
As a critical component of casting processes, the importance of runners cannot be overlooked. Good runner design is fundamental to obtaining quality castings. With technological advancements, runner technology will continue to innovate. Understanding runner principles and design methods is essential for casting engineers.